1. 지네릭스(Generics)
- 컴파일 시, 타입체크를 해주는 기능 => 타입안전성 상승
- 의도하지 않은 객체 저장 예방
- 잘못된 형변환 오류 예방
- 클래스와 메서드에 선언 가능
>>지네릭 클래스의 선언
:클래스를 작성할 때 Object 대신 T같은 타입변수를 사용
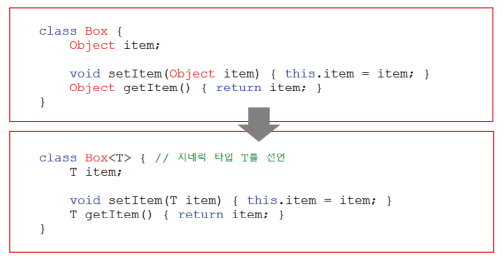
>>지네릭스 용어

=> Box<String>과 Box<Integer>는 같은 클래스이다.
=> Box<T>에 서로 다른 타입을 대입하여 호출한 것일 뿐
>>지네릭스 제한
- static 멤버에 T사용 불가 : 모든 객체에 대해 동일해야 하는데 변수가 다르기 때문

- 지네릭 타입의 배열 x => new T[10]

==> new 연산자는 컴파일 시점에 타입 T가 무엇인지 알아야 하는데 T가 어떤 타입이 될지 알수 없음
>>지네릭 클래스의 객체 생성과 사용
1) 참조변수 == 생성자에 대입된 타입

2) 상속관계일 때는 대입된 타입이 일치하는 것은 ok
ex) Box(부모) <= FruitBox(자손) 일 때

3) 대입된 타입과 다른 타입의 객체는 추가x

4) 대입된 타입의 자손 타입 객체는 추가0
| Fruit | |
| Apple | Grape |

ex)
package ch12;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class FruitBoxEx1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Box<Fruit> fruitBox = new Box<Fruit>();
Box<Apple> appleBox = new Box<Apple>();
Box<Toy> toyBox = new Box<Toy>();
// Box<Grape> grapeBox = new Box<Apple>; => 에러 : 생성자와 타입변수 불일치
fruitBox.add(new Fruit());
fruitBox.add(new Apple());
fruitBox.add(new Grape());
appleBox.add(new Apple());
appleBox.add(new Apple());
// appleBox.add(new Toy()); => 에러 : 타입불일치
toyBox.add(new Toy());
// toyBox.add(new Apple()); => 에러 : 타입불일치
System.out.println(fruitBox);
System.out.println(appleBox);
System.out.println(toyBox);
}
}
class Fruit{public String toString(){return "Fruit";}}
class Apple extends Fruit{public String toString(){return "Apple";}}
class Grape extends Fruit{public String toString(){return "Grape";}}
class Toy {public String toString(){return "Toy";}}
class Box<T>{
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
void add(T item){list.add(item);}
T get(int i){return list.get(i);}
int size(){return list.size();}
public String toString() {return list.toString();}
}
>>실행결과
[Fruit, Apple, Grape]
[Apple, Apple]
[Toy]
>>제한된 지네릭 클래스
: 지네릭 타입에 extends를 사용 => 특정 타입의 자손만 대입할 수 있게 제한

: 인터페이스의 경우에도 implements가 아닌 extends사용

ex)
public class FruitBoxEx1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FruitBox<Fruit> fruitBox = new FruitBox<Fruit>();
FruitBox<Apple> appleBox = new FruitBox<Apple>();
FruitBox<Grape> grapeBox = new FruitBox<Grape>();
//FruitBox<Toy> toyBox = new FruitBox<Toy>(); => Fruit 자손이 아니며 Eatable구현x
fruitBox.add(new Fruit());
fruitBox.add(new Apple());
fruitBox.add(new Grape());
appleBox.add(new Apple());
grapeBox.add(new Grape());
// appleBox.add(new Grape()); => Grape은 Apple의 자손이 아님
System.out.println("fruitBox-"+ fruitBox);
System.out.println("appleBox-" + appleBox);
System.out.println("grapeBox-" + grapeBox);
}
}
class Fruit implements Eatable {public String toString(){return "Fruit";}}
class Apple extends Fruit{public String toString(){return "Apple";}}
class Grape extends Fruit{public String toString(){return "Grape";}}
class Toy {public String toString(){return "Toy";}}
interface Eatable{};
class FruitBox<T extends Fruit & Eatable> extends Box<T> {};
class Box<T>{
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
void add(T item){list.add(item);}
T get(int i){return list.get(i);}
int size(){return list.size();}
public String toString() {return list.toString();}
}
>>실행결과
fruitBox-[Fruit, Apple, Grape]
appleBox-[Apple]
grapeBox-[Grape]>>와일드 카드
- 여러 타입 대입 가능

ex)
package ch12;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class FruitEx3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FruitBox<Fruit> fruitBox = new FruitBox<>();
FruitBox<Apple> appleBox = new FruitBox<>();
fruitBox.add(new Apple());
fruitBox.add(new Grape());
appleBox.add(new Apple());
appleBox.add(new Apple());
System.out.println(Juicer.makeJuice(fruitBox));
System.out.println(Juicer.makeJuice(appleBox));
}
}
class Fruit {public String toString(){return "Fruit";}}
class Apple extends Fruit{public String toString(){return "Apple";}}
class Grape extends Fruit{public String toString(){return "Grape";}}
class Juice{
String name;
Juice(String name){this.name= name+"Juice";}
public String toString(){return name;}
}
class Juicer{
static Juice makeJuice(FruitBox<? extends Fruit> box){
String tmp="";
for(Fruit f: box.getList()){
tmp+=f+" ";
}
return new Juice(tmp);
}
}
class FruitBox<T extends Fruit> extends Box<T>{}
class Box<T>{
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
ArrayList<T> getList(){ return list;}
void add(T item){list.add(item);}
public String toString() {return list.toString();}
}
>>실행결과
Apple Grape Juice
Apple Apple Juice>>지네릭 메서드
: 메서드 반환타입 앞에 지네릭 타입이 선언된 메서드
: static 메서드에는 지네릭 타입 선언이 가능
=> static 멤버는 불가능

: 호출시, 타입변수에 타입을 대입해야 함

=> 매개변수 타입이 복잡할 때 유용
<before>
public static void printAll(ArrayList<? extends Product> list, ArratList<? extends Product> list2)
<after>
public static<T extends Product> void printAll(ArrayList<T> list, ArratList<T> list2)
>>지네릭 타입의 형변환
1) 지네릭 타입 <=> 원시타입 형변환 (O)
: 다만 경고 발생

2) 지네릭 타입 <=> 지네릭 타입 형변환 (X)
Box<Object> objBox = null;
Box<String> strBox = null;
objBox =(Box<Object>)strBox; //에러! Box<String> -> Box<Object> =>지네릭간 변환x
strBox =(Box<String>)objBox; //에러! Box<Object> -> Box<String> =>지네릭간 변환x
3) 와일드 카드의 경우는 지네릭 <=> 와일드카드 형변환 가능

>>지네릭 타입의 제거
- 컴파일러는 지네릭 타입을 제거하고 필요한 곳에 형변환을 넣는다

2. Enums
- 서로 관련된 상수를 편리하게 사용하는 기능
- 값뿐만 아니라 타입도 관리 (C에서는 int로만 저장)
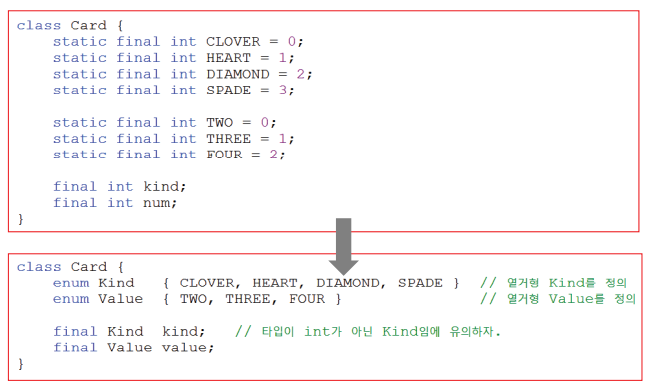
자바에서는 타입에 안전한 열거형
=> 실제 값이 같아도 타입이 다르면 컴파일 에러가 발생함
ex)
IF(Card.TWO ==Card.CLOVER) // TRUE
IF(CARD.KIND.CLOVER == CARD.VALUE.TWO) // FALSE =>타입이 다름
>>열거형의 정의와 사용
1) 열거형 정의 : enum [ 열거형 이름 ]

2) 열거형 타입 변수 사용

3) 열거형 상수의 비교에 ==와 compareTo 사용가능
: 비교연산자(><)는 사용 불가

>> 메서드 : java.lang.Enum클래스에 정의됨
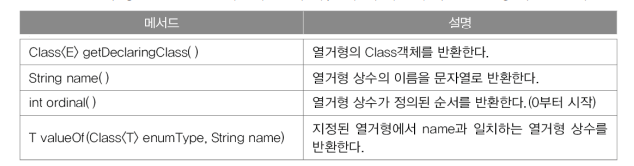
+) 컴파일러가 추가해주는 메서드들
| static E values() | 열거형의 모든 상수 반환 |
| static E valueOf(String name) | name을 가진 열거형 상수 반환 |
ex)
package ch12;
enum Direction{EAST, SOUTH, WEST, NORTH}
public class EnumEx1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Direction d1= Direction.EAST;
Direction d2= Direction.valueOf("WEST");
Direction d3= Enum.valueOf(Direction.class, "EAST");
System.out.println("d1="+d1);
System.out.println("d2="+d2);
System.out.println("d3="+d3);
System.out.println("d1==d2 ?"+ (d1==d2));
System.out.println("d1==d3 ?"+ (d1==d3));
System.out.println("d1.equals(d3) ?"+ d1.equals(d3));
// System.out.println("d2>d3 ?"+ (d2>d3)); => enum 상수끼리 비교연산자 사용 불가
System.out.println("d1.compareTo(d3) ?"+ (d1.compareTo(d3)));
System.out.println("d1.compareTo(d2) ?"+ (d1.compareTo(d2)));
switch(d1){
case EAST:
System.out.println("The direction is EAST");break;
case WEST:
System.out.println("The direction is WEST");break;
case SOUTH:
System.out.println("The direction is SOUTH");break;
case NORTH:
System.out.println("The direction is NORTH");break;
default:
System.out.println("Invalid direction");break;
}
Direction[] drr= Direction.values(); //모든 enum상수 배열 반환
for(Direction d : drr){
System.out.printf("%s=%dn", d.name(), d.ordinal());
}
}
}
>>실행결과
d1=EAST
d2=WEST
d3=EAST
d1==d2 ?false
d1==d3 ?true
d1.equals(d3) ?true
d1.compareTo(d3) ?0
d1.compareTo(d2) ?-2
The direction is EAST
EAST=0
SOUTH=1
WEST=2
NORTH=3
>> 열거형에 멤버 추가하기
- 불연속적인 열거형 상수의 경우, 원하는 값을 괄호와 함께 적음

+) 인스턴스 변수(멤버 변수)와 생성자를 새로 추가해주어야 함

- 열거형의 생성자는 묵시적으로 private이므로, 외부에서는 객체 생성이 불가함
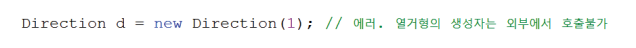
ex)
package ch12;
enum Direct {
EAST(1, ">"),SOUTH(2, "V"), WEST(3, "<"), NORTH(4, "^");
private final int value;
private final String symbol;
Direct(int value, String symbol){
this.value= value;
this.symbol= symbol;
}
private static final Direct [] DIR_ARR= Direct.values();
public int getValue(){return value;}
public String getSymbol(){ return symbol;}
public static Direct of(int dir){
if(dir<1 || dir>4){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid value : "+ dir);
}
return DIR_ARR[dir-1];
}
public Direct rotate(int num){
num%=4;
if(num<0) num+=4;
return DIR_ARR[(value+num-1)%4];
}
public String toString(){
return name()+getSymbol();
}
}
public class EnumEx2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(Direct d: Direct.values()){
System.out.printf("%s=%d%n", d.name(), d.getValue());
}
Direct d1= Direct.EAST;
Direct d2= Direct.of(1);
System.out.printf("d1=%s, %d%n", d1.name(), d1.getValue());
System.out.printf("d2=%s, %d%n", d2.name(), d2.getValue());
System.out.println(Direct.EAST.rotate(1));
System.out.println(Direct.EAST.rotate(2));
System.out.println(Direct.EAST.rotate(-1));
System.out.println(Direct.EAST.rotate(-2));
}
}
>>실행결과
EAST=1
SOUTH=2
WEST=3
NORTH=4
d1=EAST, 1
d2=EAST, 1
SOUTHV
WEST<
NORTH^
WEST<>>열거형에 추상 메서드 추가하기
- 열거형에 추상메서드를 선언하면 각 열거형 상수가 이 추상메서드를 반드시 구현해야 함
package ch12;
enum Transportation{
//무조건 추상 메서드를 구현해야 함
BUS(100) {int fare(int distance){return distance *BASIC_FARE;}},
TRAIN(150) {int fare(int distance){return distance *BASIC_FARE;}},
SHIP(100) {int fare(int distance){return distance *BASIC_FARE;}},
AIRPLANE(300) {int fare(int distance){return distance *BASIC_FARE;}};
protected final int BASIC_FARE;
Transportation(int money){
BASIC_FARE=money;
}
public int getBasicFare() { return BASIC_FARE;}
abstract int fare(int distance);
}
public class EnumEx3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("bus fare="+Transportation.BUS.fare(100));
System.out.println("train fare="+Transportation.TRAIN.fare(100));
System.out.println("ship fare="+Transportation.SHIP.fare(100));
System.out.println("airplane fare="+Transportation.AIRPLANE.fare(100));
}
}
>>실행결과
bus fare=10000
train fare=15000
ship fare=10000
airplane fare=30000>>enum 이해하기
- enum이 다음처럼 선언이 되어 있을 때

- 내부적으로는 다음처럼 작성된 것과 유사함

=> EAST, SOUTH, WEST, NORTH는 static 상수이기 때문에 객체의 주소이고 바뀌지 않으므로 '=='로 비교 가능
3. 애너테이션(annotation)
- 주석처럼 프로그래밍 언어에 영향을 미치지 않으며 유용한 정보를 저장
- 모든 프로그램에게 의미가 있는 것x / 미리 정의된 종류와 형식으로 작성해야만 의미가 있음
ex) @Test : 이 메서드를 테스트해야함으로 테스트 프로그램에게 알림

>>표준 애너테이션
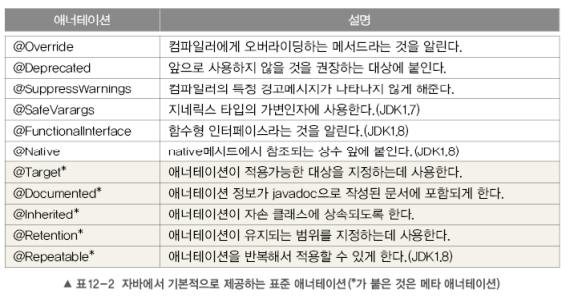
>> @Override
-오버라이딩을 올바르게 했는지 컴파일러가 체크
- 오버라이딩을 할 때, 부모 클래스에 같은 이름의 메소드가 있는지 체크
- 메서드 선언부 앞에 @Override를 붙임


>> @Deprecated
- 앞으로 사용핮 않을 것을 권장하는 필드나 메서드
- @Deprecated가 붙은 대상이 사용된 코드를 컴파일 시 => 경고 메시지 출력

package ch12;
class newClass {
int newField;
int getNewField() { return newField;}
@Deprecated
int oldField;
@Deprecated
int getOldField(){return oldField;}
}
public class AnnotationEx2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
newClass nc = new newClass();
nc.oldField=10;
System.out.println(nc.getOldField());
}
}>>@FunctionalInterface

- 함수 인터페이스에 붙이면, 컴파일러가 올바르게 작성했는지 체크
- 함수 인터페이스 : 하나의 추상 메서드만 가져야 한다는 제약
>>@SuppressWarnings
- 컴파일러의 경고메시지가 나타나지 않게 억제됨
- 괄호()안에 억제하고자하는 경고의 종류를 문자열로 지정
| deprecation | Deprecated가 붙은 대상을 사용해서 발생하는 경고 |
| unchecked | 지네릭스 타입을 지정하지 않았을 때 |
| rawtypes | 지네릭스를 사용하지 않아서 발생하는 경고 |
| varargs | 가변인자의 타입이 지네릭 타입일 때 발생하는 경고를 억제할 때 |

package ch12;
import java.util.ArrayList;
class newClass {
int newField;
int getNewField() { return newField;}
@Deprecated
int oldField;
@Deprecated
int getOldField(){return oldField;}
}
public class AnnotationEx2 {
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static void main(String[] args) {
newClass nc = new newClass();
nc.oldField=10;
System.out.println(nc.getOldField());
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ArrayList<newClass> list = new ArrayList<>;
list.add(nc);
}
}>> @SafeVarags : 가변 인자의 타입안전성
- 메서드에 선언된 가변인자의 타입이 non-reifiable타입일 경우 => non-reifiable(컴파일 후, 제거되는 타입)
- static이나 final이 붙은 메서드와 생성자에만 붙일 수 있음
- @SuppressWarnings("varargs")와 주로 함께 사용

package ch12;
import java.util.Arrays;
class MyArrayList<T>{
T[] arr;
@SafeVarargs
@SuppressWarnings("varargs")
MyArrayList(T...arr){
this.arr= arr;
}
@SafeVarargs
@SuppressWarnings("unchekced")
public static <T> MyArrayList<T> asList(T...a){
return new MyArrayList<>(a);
}
public String toString(){
return Arrays.toString(arr);
}
}
public class AnnotationEx4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList<String> list = MyArrayList.asList("1", "2", "3");
System.out.println(list);
}
}
>>메타 애너테이션
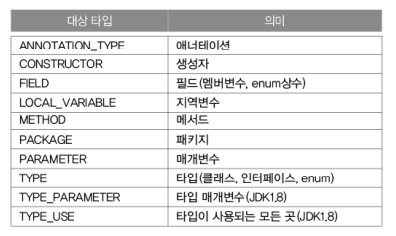
>> @Target : 애너테이션의 적용대상 지정

>>@Retention :애너테이션이 유지되는 기간
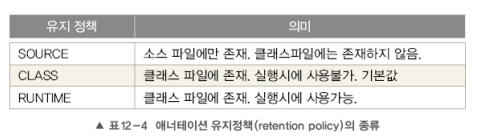
- SOURCE: 컴파일러에 의해 사용되는 애너테이션 유지 정책
- RUNTIME : 실행시에 사용 가능한 애너테이션의 정책
>>@Documented
: javadoc으로 작성된 문서에 포함

>> @Inherited
: 애너테이션을 자손 클래스에 상속하고자 할 때

>>@Repeatable : 반복해서 붙일 수 있는 애너테이션을 정의할 때
- 반복 애너테이션을 묶어서 관리할 수 있는 다른 애너테이션도 추가로 정의해야 함
@interface ToDos{
ToDo[] value();
}

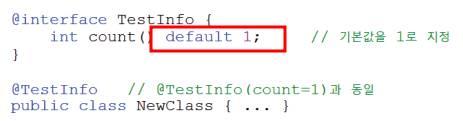
>>애너테이션 타입 정의하기

- 애너테이션의 메소드는 추상메서드이며, 적용할 때 모두 지정해야 함

@TestInfo(
count=3, testedBy="Kim",
testTools={"JUnit", "AutoTester"},
testType=TestType.FIRST,
testDate=@DateTime(yymmdd="160101", hhmmss="235959")
)
- default를 통해 기본값 지정 가능
- 요소가 하나뿐이며 이름이 value라면 이름 생략이 가능

- 요소 타입이 배열인 경우, 괄호{} 사용

@SuppressWarnings({"deprecation", "unchecked"})
=>요소 이름이 value이기 때문에 생략 가능>> java.lang.annotation.Annotation
: 모든 애너테이션의 조상이지만 상속은 불가
: 인터페이스로 정의되어 있음
: 모든 애너테이션 객체에 equals(), hasCode(), toString()같은 메서드 호출이 가능


>>마커 애너테이션
: 요소가 하나도 정의되어 있지 않은 애너테이션

>>애너테이션 요소 규칙


package ch12;
import org.w3c.dom.ls.LSOutput;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
enum TestType{FIRST, FINAL}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface TestInfo{
int count() default 1;
String testBy();
String [] testTools() default "JUnit";
TestType testType() default TestType.FIRST;
DateTime testDate();
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface DateTime{
String yymmdd();
String hhmmss();
}
@Deprecated
@SuppressWarnings("1111")
@TestInfo(testBy="aaa", testDate=@DateTime(yymmdd="160101", hhmmss="235959"))
public class AnnotationEx5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<AnnotationEx5> cls= AnnotationEx5.class;
TestInfo anno =(TestInfo)cls.getAnnotation(TestInfo.class);
System.out.println("anno.testedBy()="+ anno.testBy());
System.out.println("anno.testDate().yymmdd()="+ anno.testDate().yymmdd());
System.out.println("anno.testDate().hhmmss()="+ anno.testDate().hhmmss());
for (String str : anno.testTools()){
System.out.println("testTools="+str);
}
System.out.println();
Annotation [] annoArr =cls.getAnnotations();
for(Annotation a : annoArr){
System.out.println(a);
}
}
}
>>실행결과
anno.testedBy()=aaa
anno.testDate().yymmdd()=160101
anno.testDate().hhmmss()=235959
testTools=JUnit
@java.lang.Deprecated(forRemoval=false, since="")
@ch12.TestInfo(count=1, testType=FIRST, testTools={"JUnit"}, testBy="aaa", testDate=@ch12.DateTime(yymmdd="160101", hhmmss="235959"))
'기술 서적 > 자바의 정석' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자바의 정석] ch14-1. 람다식 (0) | 2024.02.26 |
|---|---|
| [자바의 정석] ch13. 쓰레드 (0) | 2024.02.11 |
| [자바의 정석] ch11-3.컬렉션 프레임워크 : HashMap/TreeMap / Collections (0) | 2024.01.20 |
| [자바의 정석] 11-2.컬렉션 프레임워크 : iterator / Arrays / Comparator / Set (0) | 2024.01.16 |
| [자바의 정석] ch11-1 : 컬렉션프레임워크 -- List / Stack-Queue (0) | 2024.01.14 |



